Vivinex Impress
| Vivinex Impress™ |
| Model name | XY1-EM |
| Optic design | Biconvex with square, thin and textured optic edge Anterior: Aspheric design |
| Optic & haptic materials | Hydrophobic acrylic Vivinex™ with UV- and blue light filter |
| Haptic design | Textured-rough haptic surface |
| Diameter (optic/OAL) | 6.00 mm / 13.00 mm |
| IOL Power (Spherical Equivalent) | +6.00 D to +30.00 D in increments of 0.50 D |
| Nominal A-constant* | 118.8 |
| Optimized constants** | Haigis a0 = -1.0459 a1 = 0.2547 a2 = 0.2291 Hoffer Q pACD = 5.700 Holladay 1 sf = 1.928 SRK/T A = 119.193 |
| Injector | multiSertTM preloaded |
| Front injector tip outer diameter | 1.70 mm |
| Recommended incision size | 2.20 mm |
* The A-constant is presented as a starting point for the lens power calculation. When calculating the exact lens power, it is recommended that calculations be performed individually, based on the equipment used and operating surgeon’s own experience.
** These optimized constants for the calculation of intraocular lens power published by IOLCon on their website: https://iolcon.org are calculated from 2,857 and 2,884 clinical results for Vivinex™ Models XC1/XY1 and XC1-SP/XY1-SP as of June 10, 2024. These constants are based on actual surgical data and are provided by IOLCon as a starting point for individual constant optimizations. The information available on the website is based on data originating from other users and not by HOYA Surgical Optics (“HSO”). HSO therefore does not warrant the correctness, completeness and currentness of the contents on the said website.
Information contained is intended for health care professionals. For a full list of indications and contra indications please refer to the Instructions For Use. Some of the products and/or specific features as well as the procedures featured in this document may not be approved in your country and thus may not be available there. Please contact our regional representative regarding individual availability in your country. HOYA. Vivinex, Vivinex Impress and multiSert are trademarks of the HOYA Corporation or its affiliates ©2023 HOYA Medical Singapore Pte. Ltd. All rights reserved
- HOYA data on file. CTM-23-P0105, HOYA Medical Singapore, Pte. Ltd, 2023
- HOYA data on file RnD-20-367, HOYA Medical Singapore, Pte. Ltd, 2023
- Tandogan, T. et al. (2021): In-vitro glistening formation in six different foldable hydrophobic intraocular lenses. In BMC Ophthalmol 21, 126.
- Auffarth et al. (2023) Randomized multicenter trial to assess posterior capsule pacification and glistenings in two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses. Sci Rep 13, 2822.
- Pérez-Merino, P.; Marcos, S. (2018): Effect of intraocular lens decentration on image quality tested in a custom model eye. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 44 (7), p. 889-896.
- Leydolt, C. et al. (2020): Posterior capsule pacification with two hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: 3-year results of a randomized trial. In: American journal of ophthalmology 217 (9), p. 224-231.
- Giacinto, C. et al. (2019): Surface properties of commercially available hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lenses: Comparative study. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 45 (9), p. 1330-1334.
- Werner, L. et al. (2019): Evaluation of clarity characteristics in a new hydrophobic acrylic IOL in comparison to commercially available IOLs. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 45 (10), p. 1490-1497.
- Matsushima, H. et al. (2006): Active oxygen processing for acrylic intraocular lenses to prevent posterior capsule pacification. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 32 (6), p. 1035-1040.
- Farukhi, A. et al. (2015): Evaluation of uveal and capsule biocompatibility of a single-piece hydrophobic acrylic intraocular lens with ultraviolet-ozone treatment on the posterior surface. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 41 (5), p. 1081-1087.
- Eldred, J. et al. (2019): An In Vitro Human Lens Capsular Bag Model Adopting a Graded Culture Regime to Assess Putative Impact of IOLs on PCO Formation. In: Investigative ophthalmology & visual science 60 (1), p. 113-122.
- Nanavaty, M. et al. (2019): Edge profile of commercially available square-edged intraocular lenses: Part 2. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery 45 (6), p. 847-853.
- HOYA data on file. DoF-SERT-102-MULT-03052018, HOYA Medical Singapore Pte. Ltd, 2018
- Galor, A. er al. (2013). Management strategies to reduce risk of postoperative infections. In Current ophthalmology reports, 1(4), 10.1007/40135-013-0021-5.
- Bodnar, Z. et al. (2012). Toxic anterior segment syndrome: Update on the most common causes. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery, 38(11), 1902-1910.
- Jones, J. et al. (2016). The impact of a preloaded intraocular lens delivery system on operating room efficiency in routine cataract surgery. In: Clinical ophthalmology (Auckland, N.Z.), 10, 1123-1129.
- Park, C. et al. (2018). Toxic anterior segment syndrome-an updated review. In: BMC ophthalmology, 18(1), 276.
- Chung, B. et al. (2018). Preloaded and non-preloaded intraocular lens delivery system and characteristics: human and porcine eyes trial. In: International journal of ophthalmology, 11(1), 6-11.
- Schmidbauer, J. et al. Rates and causes of intraoperative removal of foldable and rigid intraocular lenses: clinicopathological analysis of 100 cases. In: Journal of cataract and refractive surgery, 28(7), 1223-1228.
Vivinex ImpressTM enhances the intermediate vision of monofocal patients
Vivinex ImpressTM provides greater than 1 line of binocular visual acuity improvement at 66cm
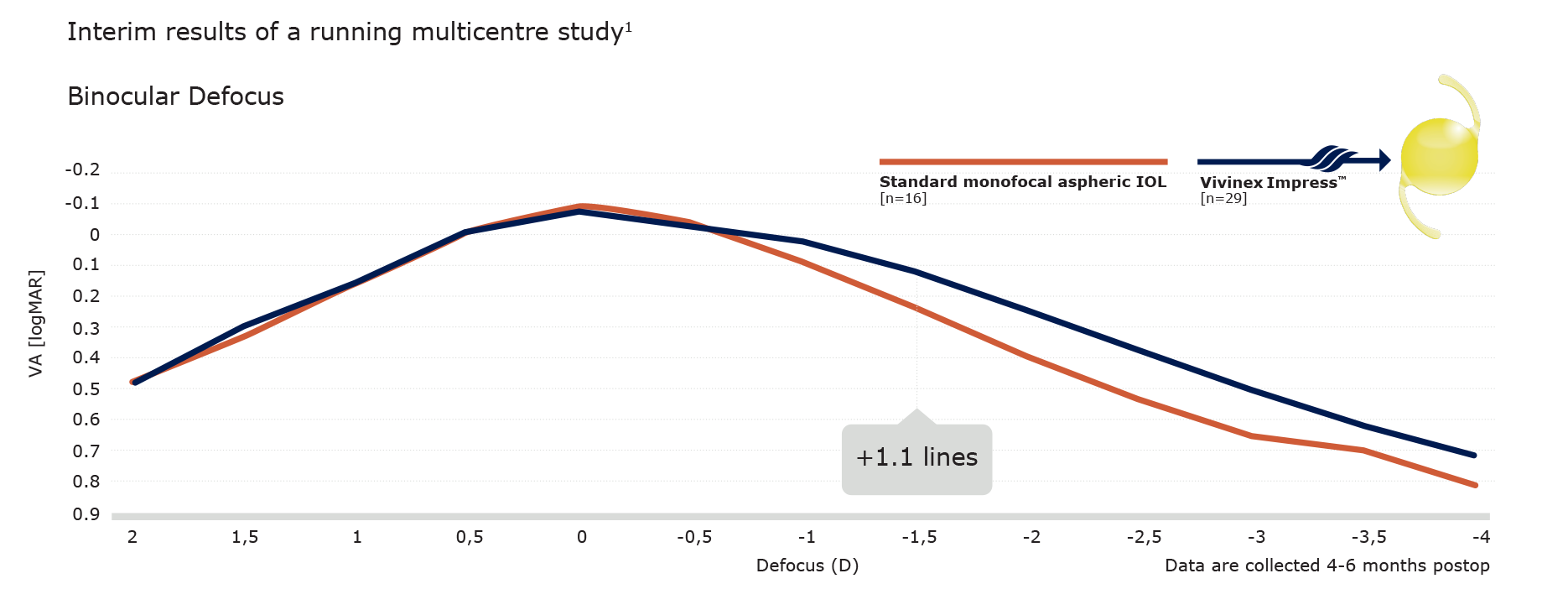
Vivinex ImpressTM provides the same best-corrected mean distance acuity as a standard monofocal aspheric IOL1
Vivinex Impress™ improves intermediate visual acuity at 66 cm (-1.5 D defocus) by more than 1 line1
Vivinex ImpressTM improves intermediate vision and provides consitant refractive predictability
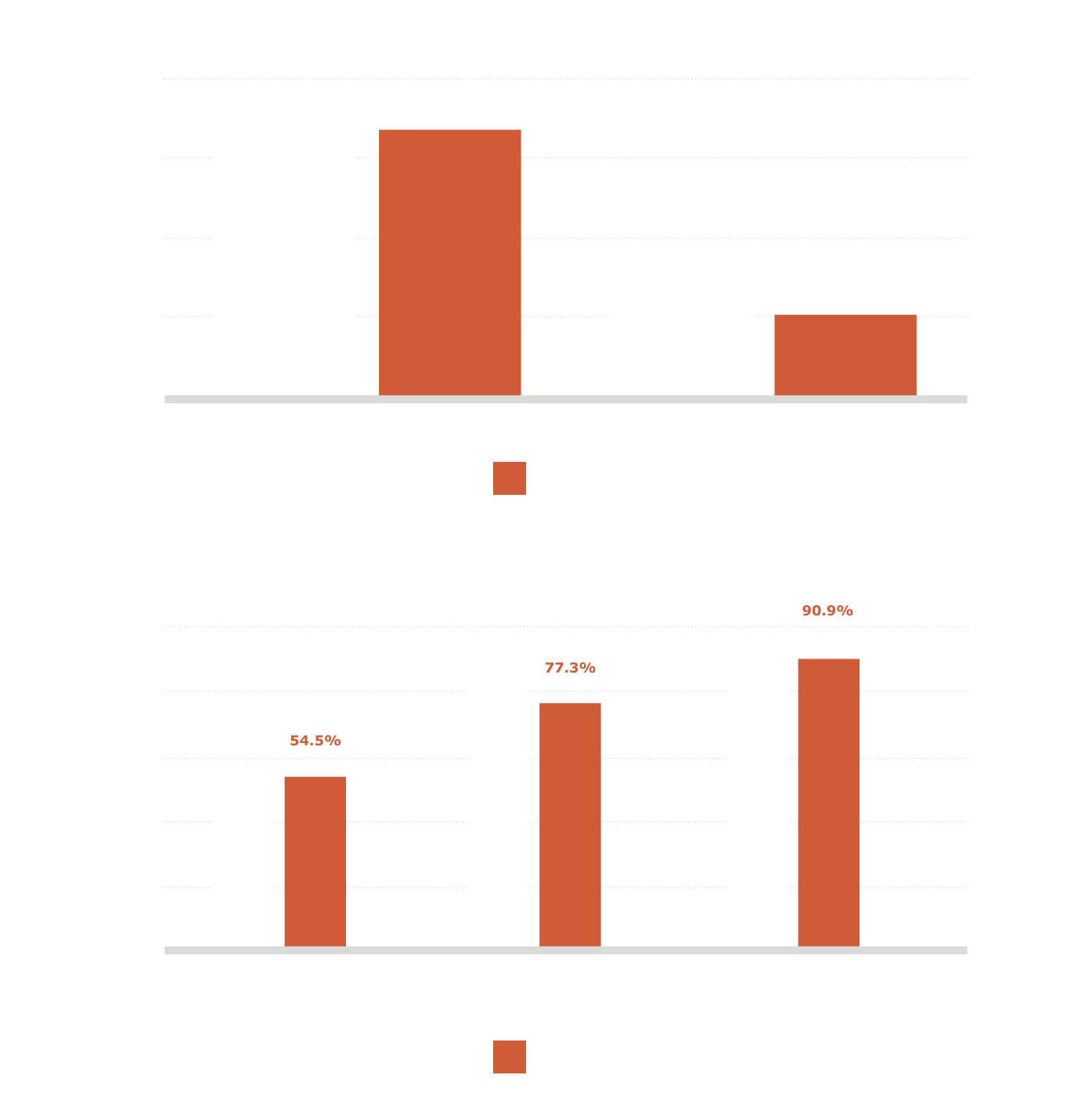
- No difference in best-corrected mean distance visual acuity at 4m between Vivinex ImpressTM and a standard monofocal aspheric IOL1
- Approximately 1 line improvement in distance- corrected visual acuity at 66cm in the Vivinex ImpressTM group1
- Refractive predictability was excellent in both Vivinex Impress™ and the standard monofocal aspheric groups1
- within 0.25D of target: 60% vs 55%
- within 0.50D of target: 87% vs 77%
- within 0.75D of target: 100% vs 91%
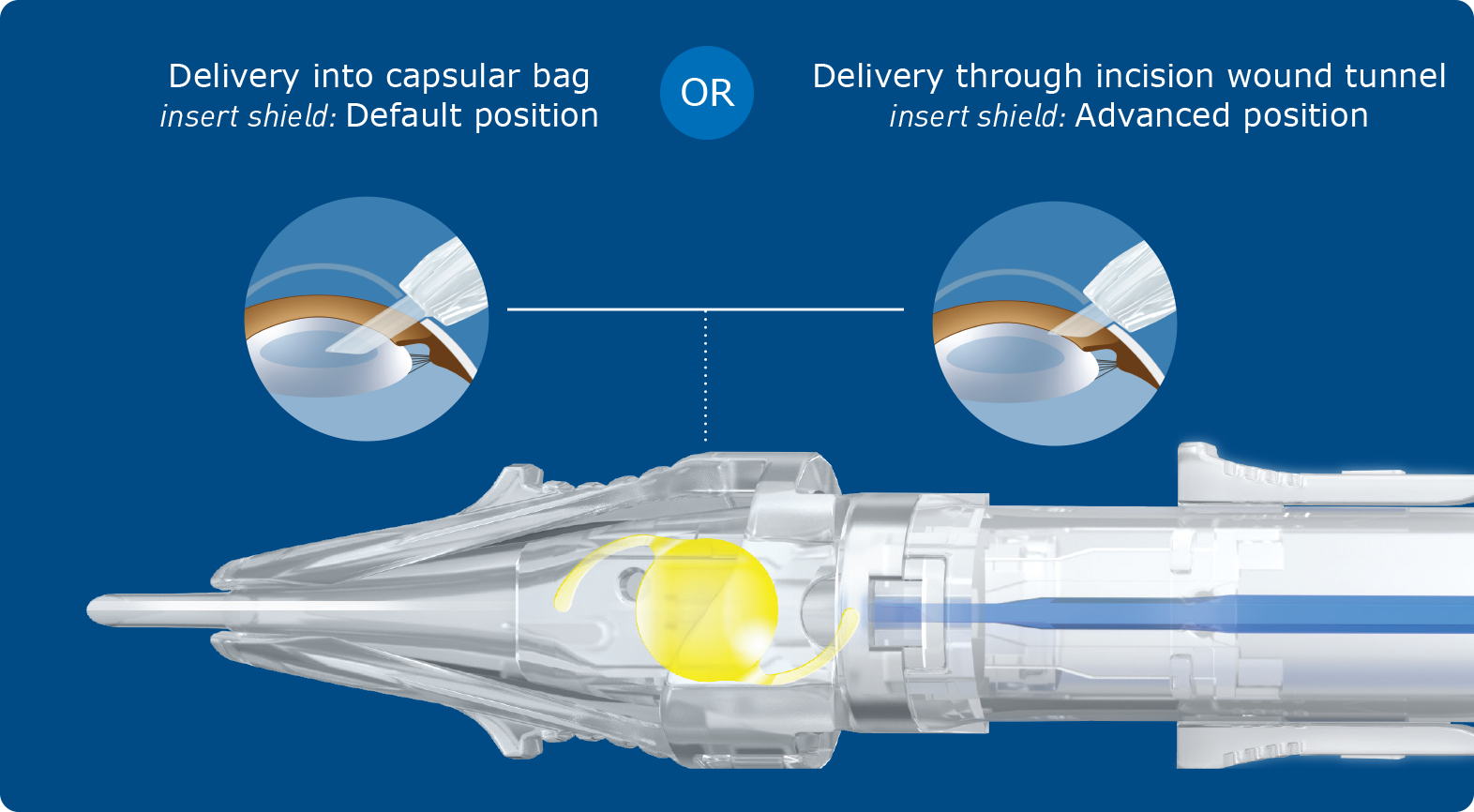
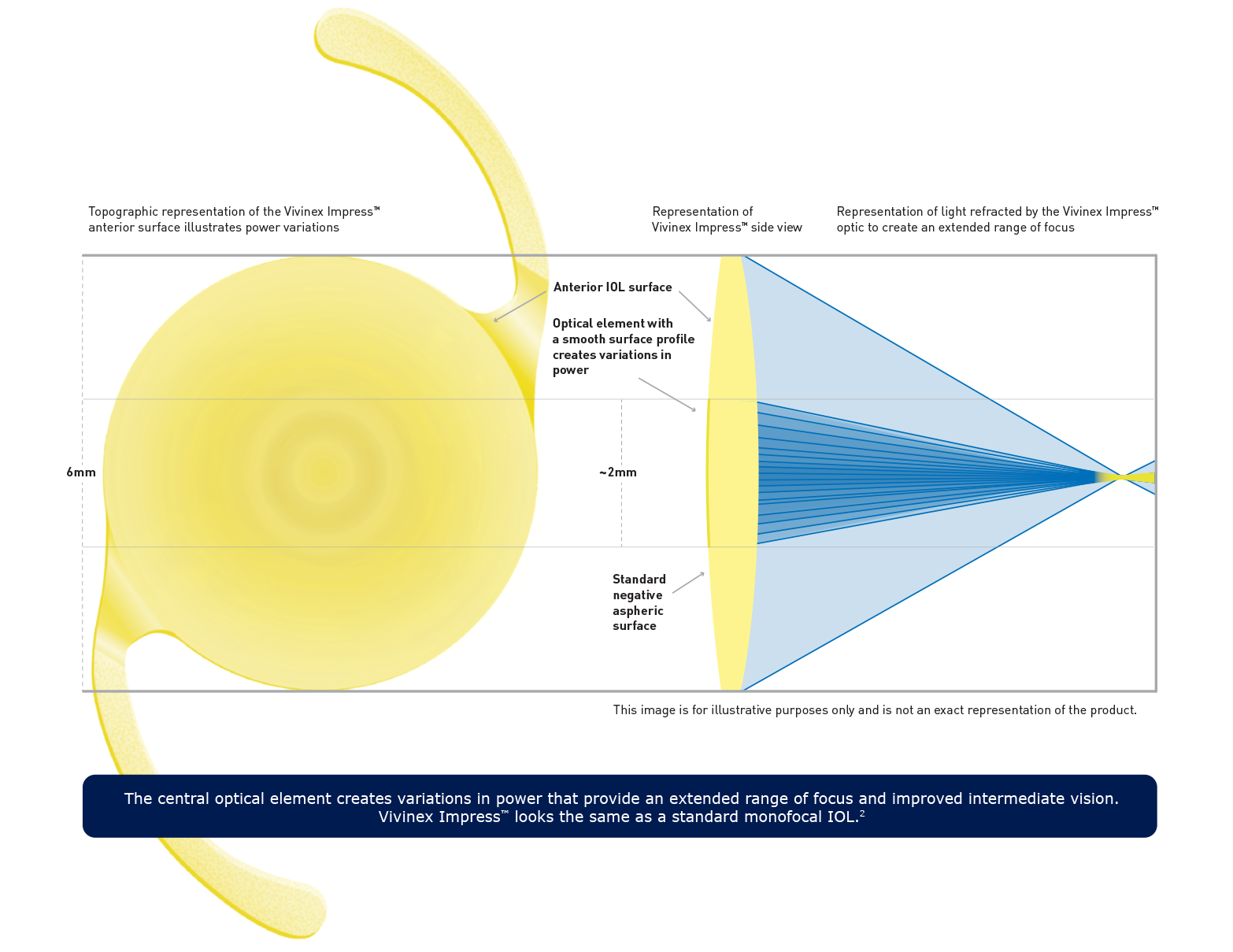
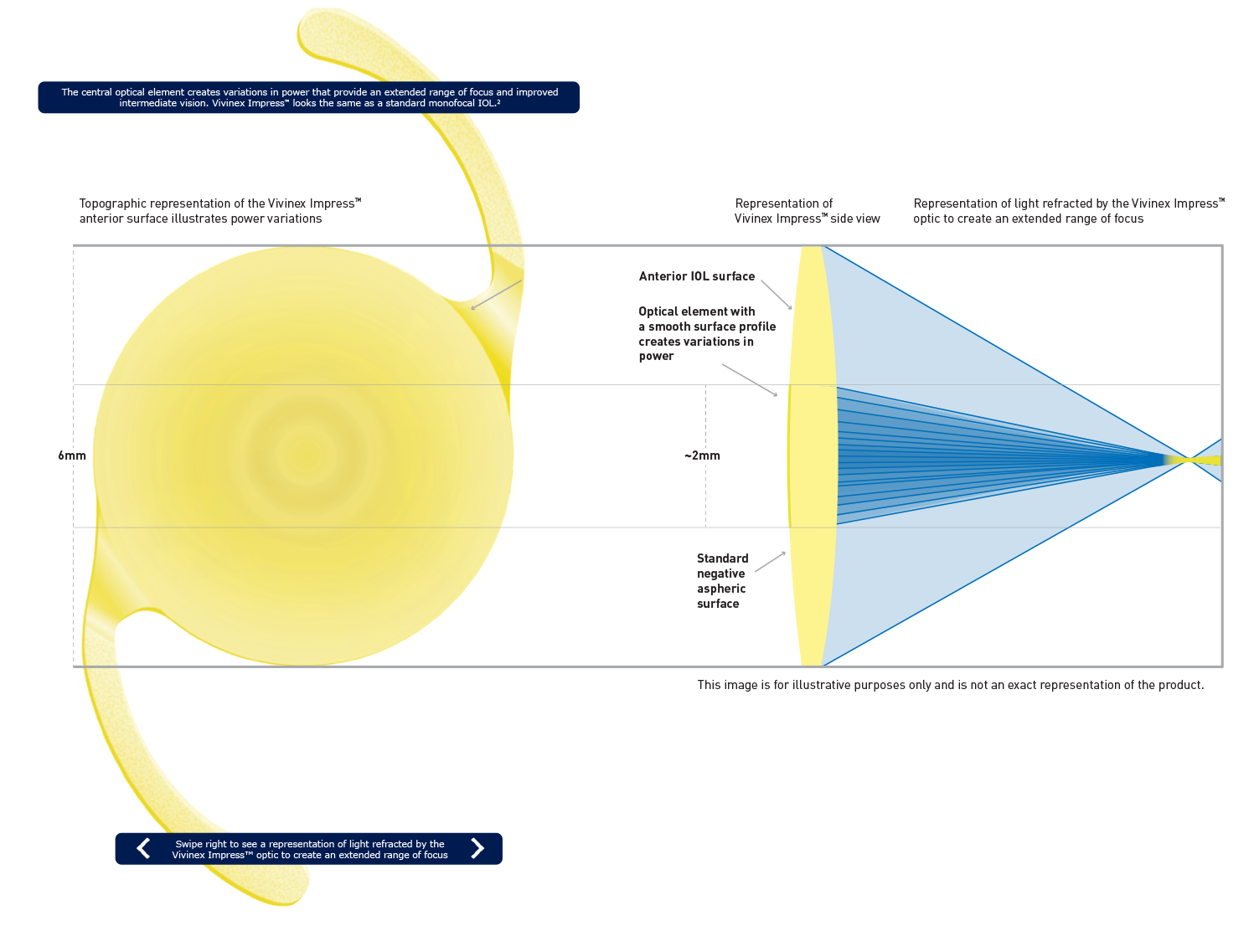
So how does Vivinex ImpressTM work?
Benefits of the VivinexTM Platform


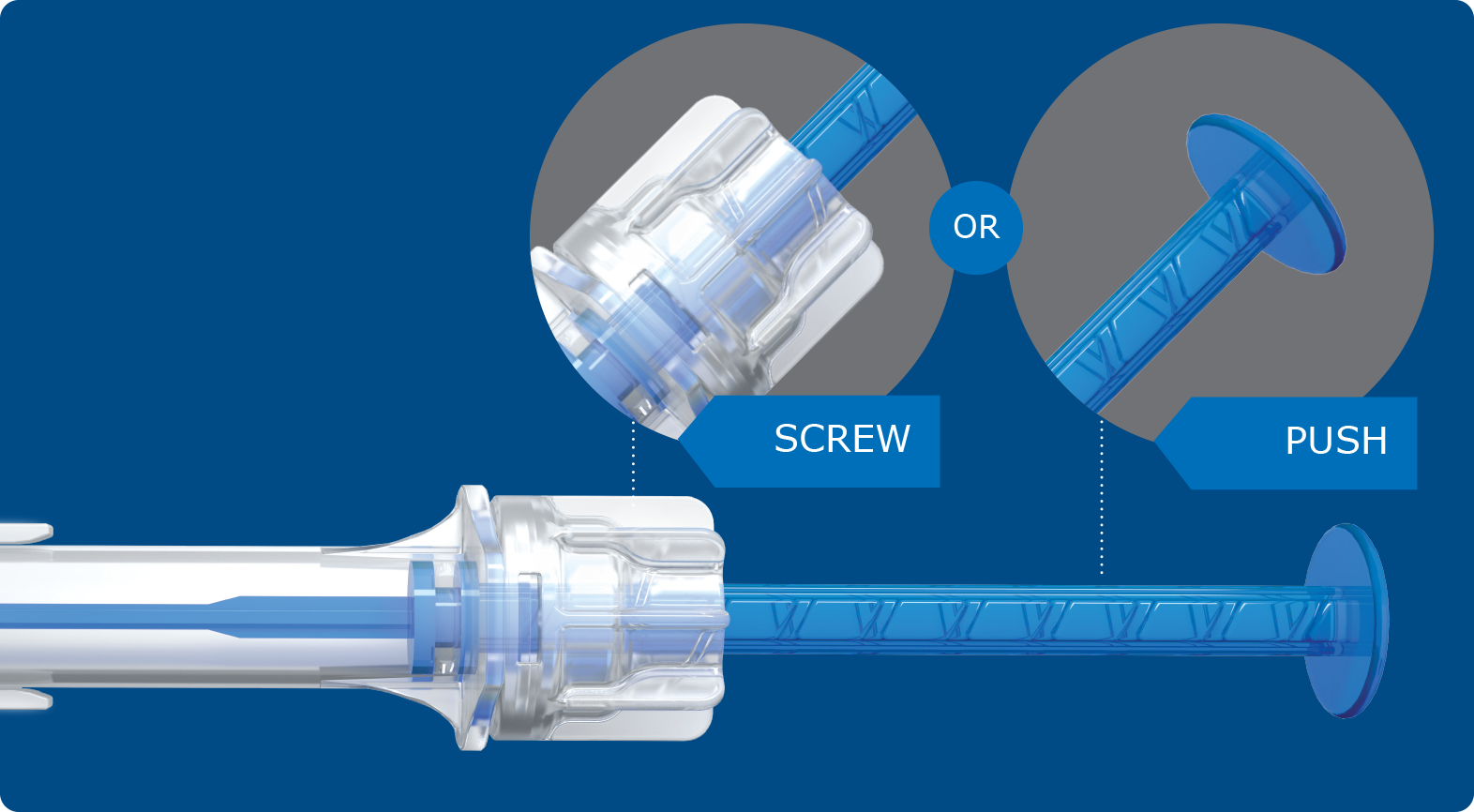
Delivered in the preloaded multiSertTM injector